Analyzing the Economic Benefits of Solar Power: Examining Cost Savings
Solar power is becoming an increasingly popular energy source due to its many economic and environmental benefits. This form of renewable energy has the potential to significantly reduce energy costs for both households and businesses. In this paper, we will analyze the economic benefits of solar power by examining the cost savings associated with its use.
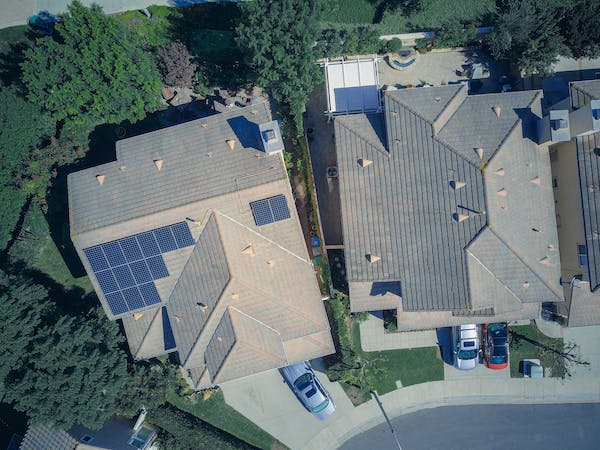
One of the primary reasons for choosing solar power is its cost saving potential. Solar energy systems require an initial investment, but the economic benefits associated with their use can far outweigh the initial cost. Many households and businesses can benefit from reduced energy bills by installing solar panels. The amount of savings depends on the size of the system, the amount of sunlight available, and the solar panel efficiency.
The cost savings associated with solar power can be further enhanced through government incentives. Many countries, states, and cities offer financial incentives and tax credits to encourage the adoption of solar energy. These incentives can significantly reduce the cost of installing solar panels and make them more affordable.
In addition to reduced energy costs, solar energy systems also provide economic benefits in terms of job creation and economic growth. The installation of solar panels creates jobs in the construction and maintenance sector. This, in turn, leads to increased economic activity in the local area and can stimulate economic growth.
Solar energy systems also have environmental benefits. Solar power helps to reduce emissions of harmful pollutants, such as carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide. This has a positive effect on air quality, reducing health risks associated with air pollution.
Overall, solar power provides numerous economic benefits in terms of cost savings, job creation, and economic growth. The cost savings associated with its use can be further enhanced through government incentives, making solar power an attractive option for many households and businesses. Additionally, the environmental benefits of solar power make it an even more attractive option for those looking to reduce their carbon footprint.
Exploring the Financial Incentives for Investing in Solar Power
The global energy landscape is undergoing a rapid transformation, and the adoption of solar power is playing an increasingly important role. Solar energy is one of the most sustainable and cost-effective sources of renewable energy, and its potential for growth has made it an attractive investment for both individuals and businesses. While the initial investment costs of solar power can be high, there are a number of financial incentives that can make solar power an attractive and lucrative investment.
At the federal level, the Solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC) offers a generous tax credit of up to 30 percent of the cost of installing a solar system. This credit is available for both residential and commercial solar installations, and has helped to make solar energy more accessible and affordable. Additionally, many states and municipalities offer additional incentives for investing in solar power, including rebates, grants, and other forms of financial assistance.
In addition to the tax credits and other incentives offered at the federal and state levels, many utility companies offer net metering programs that allow solar power users to sell any excess electricity generated back to the grid. This can significantly reduce energy bills and can even result in a profit for the solar power user. Additionally, some states offer additional incentives for investing in solar power through property tax exemptions and special financing programs.
Finally, the rising cost of traditional electricity has made solar energy more cost-effective than ever before. As the cost of electricity continues to rise, the cost savings associated with investing in solar power only increase. The combination of lower upfront costs, generous tax credits, net metering programs, and falling electricity prices make investing in solar power a financially attractive option.
In conclusion, investing in solar power can be a lucrative and financially rewarding decision. With generous federal and state tax credits, net metering programs, and declining electricity prices, solar power has become one of the most attractive renewable energy investments available. By taking advantage of these financial incentives, investors can capitalize on the long-term cost savings and economic benefits of solar energy.
Understanding the Financial Implications of Solar Power: Examining Tax Credits
The financial implications of solar power are becoming increasingly important as the technology becomes more widely used. One of the most important financial incentives for solar power is the availability of tax credits. These credits can help the user to offset the costs of installing and maintaining a solar system, making solar power more affordable and accessible.
Tax credits are a type of tax incentive that allows a taxpayer to receive a direct reduction in their tax liability. They are generally available to individuals or businesses that make qualified investments in renewable energy projects. In the case of solar power, the federal government currently offers a 26% Investment Tax Credit (ITC) for solar systems installed on residential or commercial property.
The ITC is a dollar-for-dollar reduction in the amount of income tax that an individual or business owes. The amount of the credit is equal to 26% of the cost of the system, including both the equipment and installation costs. This means that the taxpayer can reduce their tax liability by up to 26% of the cost of the solar system.
The ITC is also available for businesses that install solar systems on their property. The ITC for businesses is slightly different, as it is based on the amount of energy produced by the system rather than the cost. A business can receive a tax credit of up to 22% of the energy produced by their solar system over the course of the year.
Tax credits are an important financial incentive for those considering installing a solar system. They can significantly reduce the cost of the system, making it more affordable and accessible. It is important to understand the details of the credits available, as the amount of the credit and the eligibility requirements may vary depending on where the system is installed and who is installing it. By understanding the financial implications of solar power, including the availability of tax credits, individuals and businesses can make an informed decision about whether or not to invest in solar energy.
Evaluating the Cost-Effectiveness of Solar Power vs. Traditional Energy Sources
The cost-effectiveness of solar power versus traditional energy sources is an important issue for many countries today. With the increasing demand for energy due to population growth, the need for renewable sources of energy has become even more pressing. Solar power is one of the most promising renewable energy sources available today, and its cost-effectiveness should be evaluated in order to determine its potential as an energy provider.
When evaluating the cost-effectiveness of solar power, it is important to consider the cost of installation, maintenance, and operation. Solar power systems require a large upfront investment, but the cost of installation can be offset by government incentives and other financial assistance. In addition, the cost of maintenance and operation is generally lower than that of traditional energy sources. This is because solar power systems are largely automated and, once installed, require very little intervention in order to remain functional.
The cost-effectiveness of solar power must also be evaluated in terms of its energy output. Solar power systems typically generate a lower amount of energy than traditional energy sources, but the energy they generate is often more reliable and consistent. This is due to the fact that solar energy is not affected by power outages or fluctuations in energy supply. Solar power systems also have the potential to generate energy even when traditional energy sources are unavailable, making them an ideal choice for areas with limited or unreliable access to traditional energy sources.
Finally, the environmental impact of solar power must also be taken into consideration when evaluating its cost-effectiveness. Solar power systems are a clean and renewable energy source and produce no emissions or pollutants. This makes them an attractive choice for those looking to reduce their environmental footprint and contribute to the global effort to combat climate change.
In conclusion, the cost-effectiveness of solar power must be evaluated on a case-by-case basis. Factors such as the cost of installation, maintenance, and operation, as well as the energy output and environmental impact, must all be taken into account. While solar power can be an expensive investment, its long-term cost-effectiveness and environmental benefits make it an attractive option for many countries today.
Exploring the Long-Term Return on Investment for Solar Power Installations
The long-term return on investment (ROI) of a solar power installation is an important factor for those considering transitioning towards renewable energy. Solar power has become increasingly accessible over the past decade, and as such, it is essential to understand the long-term financial implications of choosing this source of energy.
When considering the ROI of a solar power installation, it is important to consider the upfront cost of the system. This cost is typically spread out over several years, as the solar panels and installation must be paid for up-front. Additionally, installation costs can vary depending on the size and complexity of the system. As a result, it is important to conduct thorough research when deciding on a solar power installation.
Once the system is installed, there are several factors that contribute to the long-term ROI of solar power. First, the cost of electricity generated by the solar panels can be significantly cheaper than traditional energy sources. Solar energy is free, so the only cost associated with the energy is the cost of the installation and maintenance. Additionally, many states and local governments offer financial incentives for those who choose to install solar panels, which can help offset the upfront cost of the system.
In addition to the cost of energy, there are also tax incentives available for those who install solar power. Many states offer property tax exemptions for solar installations, which can help to reduce the long-term costs associated with the system. Additionally, the federal government offers a tax credit for those who install solar power, which can help to reduce the overall cost of the system.
Finally, the long-term ROI of a solar power installation is also affected by the life expectancy of the system. Solar panels typically last for 25-30 years, meaning that the energy produced by the system will continue to be free over that time period. This can result in a substantial long-term return on investment, as the energy produced will be completely free after the initial installation costs have been paid off.
Overall, solar power installations can provide a significant long-term return on investment. By conducting thorough research into the upfront costs and long-term incentives available, those considering transitioning to solar power can ensure that they make an informed decision. With the right research and planning, solar power can be a great choice for those looking to invest in renewable energy.