The Myth of Solar Energy Requiring Perfectly Sunny Days
Solar energy has long been viewed as an unreliable source of energy, due to its dependence on sunny weather. This is a misconception, however; solar energy can be effectively used regardless of the weather. Solar energy is generated through the use of photovoltaic cells, which absorb energy from the sun’s rays. This energy is converted into an electrical current, which can be used to power a home or business.
The amount of solar energy that can be generated is not dependent on the weather conditions; it is instead dependent on the amount of sunlight that is available. Even on a cloudy day, the photovoltaic cells can still absorb energy from the diffuse light. In fact, some studies have shown that the efficiency of solar systems actually increases on cloudy days, due to the softer, more diffuse light.
The myth of solar energy requiring perfectly sunny days is further debunked by the fact that most solar systems are equipped with storage batteries. These batteries store the energy that is generated during the day, so that it can be used at night or during periods of low sunlight. This allows for a continuous supply of solar energy, even when the sun isn’t shining.
In conclusion, solar energy does not require perfectly sunny days in order to be effective. Photovoltaic cells are able to absorb energy from the sun’s rays even on cloudy days, and storage batteries can provide a continuous supply of energy even when the sun isn’t shining. Solar energy is therefore a reliable source of energy, regardless of the weather.
The Myth That Solar Panels Damage Your Roof
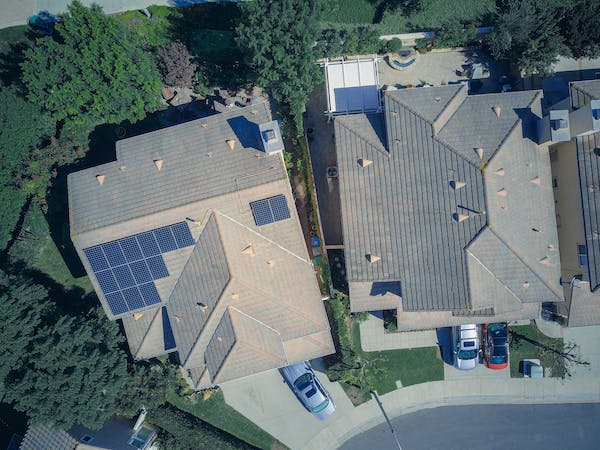
The idea that solar panels can damage a roof has been circulating for some time, but there is no scientific evidence to suggest that the installation of such panels has a negative effect. Solar panels are designed to be installed on a roof in such a way that their weight does not compromise the integrity of the roof structure. Furthermore, solar panel installation requires the use of a mounting system and fasteners that are specifically designed to secure the panels in place without causing any damage.
In some cases, however, the installation of solar panels may require some modifications to the existing roof structure. This is usually done to ensure that the panels are securely attached to the roof. Additionally, the roof may need to be reinforced to support the extra weight of the panels and their mounting system. Such modifications are typically minor, and they are necessary to ensure both the integrity of the roof and the safety of the occupants.
In conclusion, there is no scientific evidence to suggest that solar panels cause any damage to a roof. On the contrary, the installation of such panels requires modifications to the roof structure that are necessary to ensure the roof’s structural integrity and the safety of its occupants. Therefore, it can be said that the myth that solar panels damage a roof is unfounded.
The Myth That Solar Panels Are Too Expensive to Install
The idea that solar panels are too expensive to install is a pervasive myth. In reality, the cost of solar panels has decreased significantly over the past few years, making them a much more affordable option for homeowners. In addition, many governments offer incentives to encourage people to switch to solar, such as tax credits and discounted installation costs.
When considering the cost of solar panels, it is important to consider the long-term savings that they can provide. Solar panels can significantly reduce a household’s energy costs, as they produce electricity without any additional fuel. This means that homeowners can save money on their electricity bills over time. Additionally, some utility companies offer net metering, which allows solar panel owners to sell excess electricity back to the grid. This can help to offset the initial cost of installation even further.
When deciding whether or not to install solar panels, it is important to consider the total cost of ownership. This includes the purchase price of the solar panels, installation fees, and any rebates or tax credits that may be available. Taking all of these factors into account can help to determine the overall cost of solar panel installation.
In conclusion, the myth that solar panels are too expensive to install is simply not true. The cost of installation has dropped dramatically in recent years and there are a number of financial incentives available to help make solar panel installation more affordable. It is important to consider all of the costs associated with solar panel installation, as well as the potential long-term savings that they can provide.
The Myth That Solar Panels Take Up Too Much Room
The notion that solar panels take up too much room is a common misconception. In reality, modern solar panels require a much smaller area than many people assume. Advances in solar technology have made it possible to produce solar panels that are more efficient and require less physical space than ever before.
The amount of space a solar power system requires depends on the size of the system. Generally, a 2 kilowatt system will require about 20 square meters of space for a rooftop installation. This can be further minimized if the system is ground mounted.
In addition, solar panels can be installed on rooftops without taking up the entire roof. For example, a south-facing rooftop installation may take up only a fraction of the available space. This allows homeowners to still use their roofs for other purposes such as rainwater collection or recreational activities.
It is also possible to install solar panels in a way that minimizes their visual impact. This can be done with careful positioning and proper selection of panel styles. For example, mounting panels on the east or west side of a roof can be an attractive way to reduce the visual impact of the system.
Finally, it is important to note that solar panels are not permanent fixtures. Solar systems can be removed or relocated if necessary, allowing homeowners to easily adjust the amount of space they are using for solar power.
In conclusion, solar panels do not take up too much room. The amount of space required for a solar power system depends on the size and type of the system, as well as the installation method. With careful planning and careful selection of panel styles, it is possible to minimize the physical footprint of a solar power system.
The Myth That Solar Energy Is Unreliable and Unpredictable
The myth that solar energy is unreliable and unpredictable is one that is often cited by those who are skeptical of the viability of solar energy. However, upon closer examination, this myth is easily debunked.
To begin with, the reliability of solar energy is demonstrated by its widespread use around the world. In fact, according to the International Energy Agency, in 2019 solar energy accounted for almost 3 percent of global electricity production. This demonstrates that solar energy has become a reliable and viable form of energy production.
Furthermore, solar energy is not as unpredictable as some may suggest. Solar energy is, in fact, predictable due to its correlation with the sun. Solar energy production can be predicted through the use of sophisticated weather and climate models that can accurately predict when and how much energy will be produced. Additionally, solar panels can be installed in areas where the amount of sunlight is known, thus reducing any uncertainty that may exist.
Lastly, the reliability of solar energy can be further enhanced through the use of battery storage systems that enable solar energy to be stored and used when needed. This reduces the need for energy from other sources and ensures that solar energy can be used in a consistent and reliable manner.
In conclusion, the myth that solar energy is unreliable and unpredictable is simply not true. Solar energy has become a reliable and viable source of energy production, and its predictability can be enhanced through the use of sophisticated weather and climate models and battery storage systems. Thus, solar energy is a reliable and viable source of energy that is an important part of the future of energy production.